How Solar Works
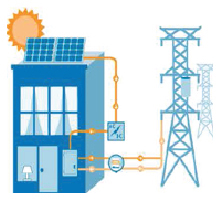
We can change sunlight directly to electricity using solar cells. Every day, light hits the solar panels with photons (particles of sunlight). The solar panel converts those photons into electrons of direct current ("DC") electricity. The electrons flow out of the solar panel and into an inverter and other electrical safety devices. The inverter converts that "DC" power (commonly used in batteries) into alternating current or "AC" power. AC power is the kind of electrical that your television, computer, and toasters use when plugged into the wall outlet. Alset Power Company has the ability to improve the efficiency of the inverter that converts the DC electricity into AC electricity. In many cases we can increase the efficiency by as much as 50% thereby providing an exponential increase in power and savings to the power company and ultimately the consumer.
A net energy meter keeps track of the all the power the solar system produces. Any solar energy that is not used simultaneous with production will go back into the electrical grid through the meter. At night or on cloudy days, when the system is not producing more than the building needs, the power user will consume electricity from the grid as normal. The utility will bill you for the "net" consumption for any given billing period and provide you with a dollar credit for any excess during a given period.
Solar Cells
Solar cells are small, square-shaped panel semiconductors made from silicon and other conductive materials, manufactured in thin film layers. When sunlight strikes a solar cell, chemical reactions release electrons, generating electric current. Solar cells are also called photovoltaic cells or "PV cells" and can be found on many small appliances such as calculators.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) System Components

A PV system components include PV modules (groups of PV cells), which are commonly called PV panels; one or more batteries; a charge regulator or controller for a stand-alone system; an inverter to covert solar power from direct current (DC) to the alternating current (AC) of the utility grid-connected system; wiring; and mounting hardware or a framework. A PV module arranges individual PV cells, and the modules are grouped together in an array. Some of the arrays are set on special tracking devices to follow sunlight all day long and improve system efficiency. Again, Alset Power Company has the ability to increase the efficiency of the inverter up to 50% in order to produce more electricity from the same components used in the solar photovoltaic system.
PV System Installation, Maintenance, and Longevity

You could install a photovoltaic (PV) or solar electric system yourself. But to avoid complications or injury, you will probably want to hire a reputable professional contractor with experience installing solar systems. While they are sophisticated electric systems, PV systems have few moving parts, so they require little maintenance. The basic PV module (an interconnected, enclosed panel of PV cells) has no moving parts and can last more than 30 years while requiring little maintenance. The components are designed to meet strict dependability and durability standards to withstand the elements. The best way to ensure and extend the life and effectiveness of your PV system is by having it installed and maintained properly. Most PV system problems occur because of poor or sloppy system installation. Some states provide warranties for systems installed under their guidelines.

Sunlight Requirements for PV Systems
A photovoltaic (PV) system needs unobstructed access to the sun's rays for most or all of the day to be effective. Shading on the system can significantly reduce energy output. Climate is not a major concern because PV systems are relatively unaffected by air temperatures, and snow cover typically melts quickly because panels are positioned directly into the sunlight. Abundant year-round sunshine makes solar energy systems useful and effective nearly everywhere in California, Arizona, Nevada, and many other states and countries with abundant sunshine.
Other Solar Technologies
- Concentrating solar power (CSP) systems concentrate the sun's energy using reflective devices such as troughs or mirror panels to produce heat that is then used to generate electricity.
- Solar water heating systems contain a solar collector that faces the sun and either heats water directly or heats a "working fluid" that, in turn, is used to heat water.
- Transpired solar collectors, or "solar walls," use solar energy to preheat ventilation air for a building.